
Bachelor’s thesis
Boolean Satisfiability problems (SAT) consists of finding a valid assignment (model) for a set of Boolean variables. It was the first problem proven to be NP-Complete which allowed reducing many NP-Complete problems to it. Because of this, it is one of the pillars of Computer Science.
An extension to SAT is Pseud-Boolean optimization problems. Unlike SAT, which can only express binary relationships among variables, Pseudo-Boolean optimization can formalize more complex relationships. These problems are defined in the following manner:
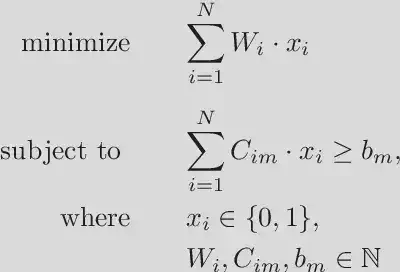
Example: Knapsack problem
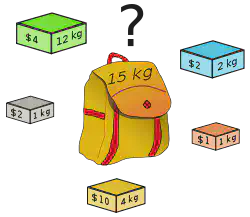
Given a set of items, each one with a value and a weight, and a knapsack with a maximum capacity, the goal is to select some objects to put inside the knapsack in a way that the weight is not bigger than the knapsack’s capacity and the total value is maximised.
The variables for this problem, given $n$ objects, are: $$o_1, o_2, \ldots , o_n \text{for the objects}$$ $$w_1, w_2, \ldots , w_n \text{for the weights}$$ $$v_1, v_2, \ldots , v_n \text{for the values}$$ There is only one constraint which represent the maximum capacity of the knapsack problem: $$w_0 o_0 + w_1 o_1+ \ldots w_n o_n \leq knapsack’s \ capacity$$ And the cost function: $$v_0 o_0 + v_1 o_1+ \ldots v_n o_n $$
SAT Solvers
A SAT solver is a tool that aims at solving Boolean Satisfiability problems. However, they take as input Boolean formulas in Conjunctive Normal Form (CNF). In this project, we propose an efficient encoding for converting Pseudo-Boolean minimisation problems into CNF constraints. If this encoding is not efficient, the size and difficulty of the problem can increase exponentially.
Proposed encoding
The proposed encoding is based on the idea that if a function’s primes cover a small space then a lot of clauses will be required when encoding it into a CNF. For more details see the slides.